Fixtures or jigs? The two words are easily mixed up. They are frequently seen together, and while possessing similar roles, the two are not interchangeable. Let us examine how these manufacturing tools are utilized to increase production quality, cut operational costs, and automate operations to discover the minor distinctions between them. Let’s examine some definitions, applications, methods of operation, purposes, and other factors.
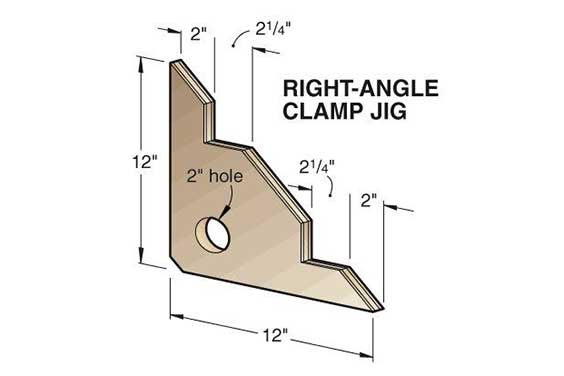
A jig is a form of custom-made work gripper used to regulate the position and movement of parts as well as other tools. Throughout the CNC machining process, a jig frequently finds and holds the workpiece in a perfect place and directs the cutting tool to perform a specific operation, in order to maintain the right link between the task and cutter. The tool remains motionless while the jig moves. Clamping is commonly used to secure the machining item in the jig.

The most popular form of jig is the drill jig used to direct the drill bit while drilling holes in specified areas. Drill jigs include the box jig, angled plate jig, sandwich jig, and channel jig. Carpentry jigs are also commonly used to create complex wooden profiles. Other sorts of jigs include;

Jigs are frequently used in drilling, reaming, counterboring, tapping, and other one-dimensional operations, or as guidance for tools or templates in other industries, such as furniture, where specific cramp jigs that assure squareness are frequently set up. Drill bushing is another typical use for jig, which helps guide a power drill through the surfaces of a machined component for proper placement and angle.

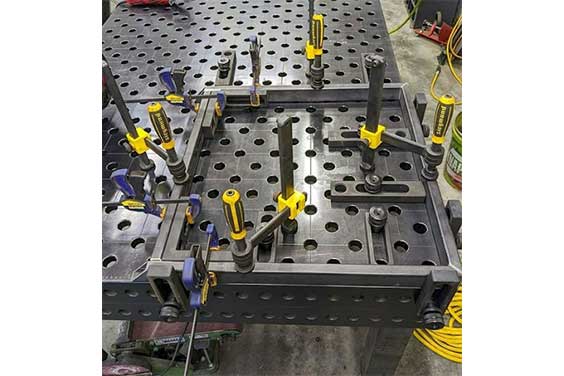
A fixture is a work-holding device that is used to firmly locate, support, and mount the component to be machined with the machine in the proper position, ensuring that the workpiece set in the fixture may retain conformance and versatility. When the fixture moves, so do the tool in relation to the component.
Fixtures can assure the stability of the component and ease the installation of the workpiece, resulting in a rapid transition from section to section and smooth running. A fixture differs from a jig in that it seldom directs the tool.
Fixtures are classified as turning fixtures, machining fixtures, grinder fixtures, broaching fixtures, drill fixtures, tapped fixtures, welder fixtures, and assembly fixtures depending on the operation to be performed.
Fixtures are frequently used in milling, rolling, drafting, slotting, grinder operations, and other multifunctional machining operations, as well as auto assembly and optical, laser scanning inspection. The material block secured within a CNC machine, as well as the vice on the workstation, is a fixture. Fixtures are also required in an automotive assembly line to secure and guide vehicles throughout the welding and assembling process.
| JIGS | FIXTURES |
| The phrase “jig” may be familiar from your weekend fishing sport, but it has a distinct connotation in the engineer’s lexicon. A jig is a tool that maintains the positioning of a tool in order to accomplish a manufacturing operation. When drilling and tapping holes, it is frequently necessary to use a bespoke component to assure precision and repeatability. Drill bushings are a typical use for jigs. They aid with the proper placement and angle of a drill as it passes through a material. A drill bushing not only leads to greater quality work but may also enhance production speed. |
What distinguishes a fixture from a jig? Fixtures, as opposed to directing a production tool, retain a workpiece in a stable position, orientation, or location. Fixtures are important industrial equipment that allows for automation. It would be difficult to discover an automated industrial process that did not need fixtures.A vehicle assembly line, for example, would not be feasible without the laborious fixtures that hold and guide automobiles through the soldering and assembly process. They could also be used to keep a product in place while optical and laser scanning is being performed to check production quality. A trip around a manufacturing plant is certain to reveal a fixture or two. |
| Jigs are generally utilized to direct the movement of the cutter at predetermined areas on the job while also supporting and locating the component. | Fixtures are mostly used to hold, support, and identify the workpiece while maintaining a preset orientation, rather than to guide the cutter. |
| Jigs are typically easy to use | whereas fixtures are more sophisticated and may require certain knowledge and accessories to use. |
| Jigs are often lower in weight for easier handling | whereas fixtures are typically heavier and must endure cutting force and vibration. |
| Jigs are not fixed to the worktop and can be held by hand without holding in machining; they could also be fastened for hard labor and do not require any additional equipment | whereas fixtures have always been clamped strongly on the workbench of a Machine tool and necessitate accessories such as blocks or gauges to precisely move the cutter. |
| Jigs are relatively more costly than fixtures | Fixtures are generally less costly than jigs. |
| The jig’s structure is frequently more complex | The fixture layouts are easier. |

The use of jigs and fixtures in tandem aids in achieving the manufacturing accuracy necessary for goods to work correctly. Examine your doors, cabinets, and shelves. The openings for the door’s knob, latch, and hinges need exact positioning or drilling instructions. The same is true for cabinets with dovetail cuts or shelf holes on the cupboard sides. Books would fall off the shelf without jigs and fittings, drawers would be fragile, and doors would not shut correctly.

Because quantities are generally modest, CNC machining is the most frequent production technique for making jigs and fixtures. When the geometry is too complex or expensive to manufacture, 3D printing is the most logical technique. It should be noted that not all jigs and fixtures must be constructed of metal. Plastic will save you money while meeting your performance requirements in numerous situations.
Rapid manufacturing will not replace your present machine shops, but it may be a helpful tool for creating blanks for jigs and fixtures or less essential parts that do not require high accuracy when used appropriately.
We suggest our CNC machining capability for your most frequent jigs or fixtures for a small number of pieces. We propose 3D printing if your item has more complicated geometry that is difficult to manufacture. Rapid injection molding can manufacture 25 to 10,000+ components in a variety of engineering-grade thermoplastics for large volume requirements.
The main difference between a jig and a fixture would be that a jig is a device used to control the positioning or movement of another tool. A fixture, on the other hand, is a support or work piece used to keep work in place. Jigs and fittings are vital equipment in metalworking and carpentry.
Now that you know the major differences and usages of the jigs and fixtures, you can now know what to use either for, and how to interuse them for optimal results.
+86-755-8524 1121
marketing@rydtooling.com
No. 2, HongKan 1st Road, YanChuan Community, YanLuo Street, BaoAn District, ShenZhen City, China. Post Code 518105.
Subscribe to our newsletter to get manufacturing news and updates!
