
Insert Molding Process Step by Step
It is dangerous to make use of components after they’ve been manufactured without encasing them with plastic. It’s essential to encase these components to make
Share
Share
When examining plastic injection mold design, tool fabrication, and effective manufacturing of molded plastic goods, the different steps of the injection molding process are scrutinized. Project management led by experience and precision scheduling is needed for optimal custom injection molding.
China injection mold makers and tool engineers are at the forefront of molding products and tool design respectively. Eventually, they are responsible for making judgments and leading the procedures required to assure uniform and reproducible workability of complication-free injection molded components.
There are several aspects and configurations to consider, and the primary goal of this essay is to discuss them. Read on to find out more.
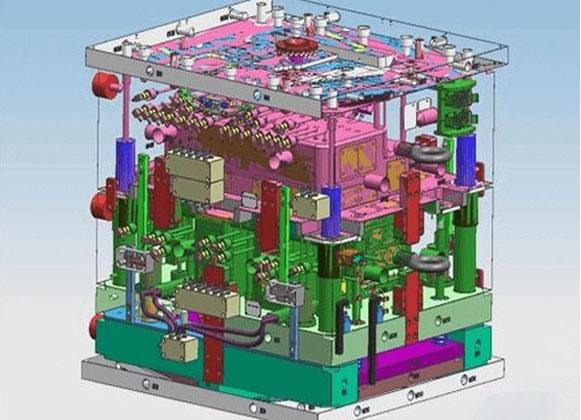
Source: Pinterest
Injection molding is the process of producing molded objects by injecting molten plastic ingredients into a mold and afterward cooling and hardening them. The technology is well-suited for mass manufacturing of goods with complex forms, and it is widely used in the field of plastic processing. There are several things to learn about how to make a plastic mold prototype;
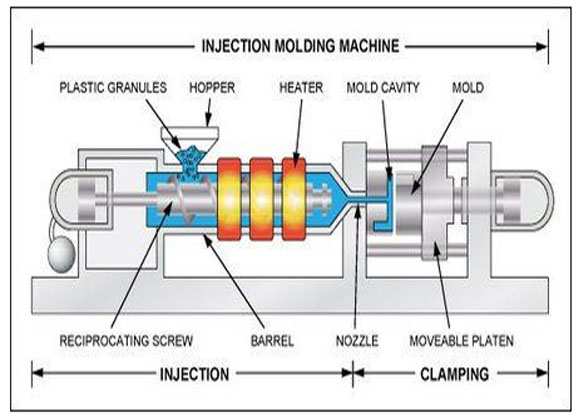
Source: Pinterest
The injection molding machine is separated into two sections: the clamp unit and the injection section. The clamp unit’s function includes entry and exit of the die and plastic item ejection. There are two sorts of clamping techniques: the toggling type and the straight-hydraulic method, where a mold is opened and shut directly using a hydraulic system.
The injection unit’s operations are melting plastic using heat and later injecting the molten material into the mold. The screw is spun to melt the polymer received from the hopper and collect molten plastic in front of the screw. The injection procedure begins once the appropriate amount of molten plastic has been collected.
The machine regulates the movement speed of the screws or injecting speed, as molten plastic flows in a mold. It also regulates dwell pressure once the molten plastic has filled holes. When either the screw level or the injection pressure reaches a particular predetermined value, the placement of transition from variable speed to pressure control is established.
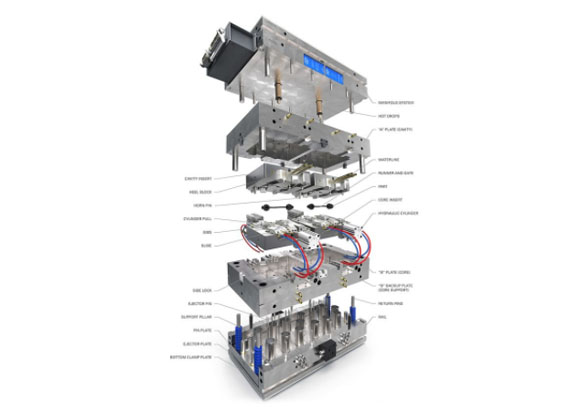
Source: Pinterest
A mold is a hollow steel block within which molten plastic is poured to form a specific fixed shape. There are several holes punched in the block for temperature adjustment through hot water, oil, or heaters.
Molten material enters a mold via a sprue and occupies cavities via runners and gates. The mold would then be reopened after the solidification process, during which the injection molding machine’s ejector rod drives the mold’s ejector panel to further expel moldings.

Source: Pinterest
Molding is made up of sprue for introducing molten resin, a runner for directing it to cavities, and products. Because producing only one product in a single shot is wasteful, a mold is generally constructed with many holes linked by a runner so that other products may be produced in a single shot.
If indeed the distance of the runner towards each cavity differs in this scenario, the cavities might not get filled concurrently, resulting in varied dimensions, looks, or characteristics of the molding cavity by cavity. As a result, the runner is often constructed to be the same distance from the sprue to all the cavities.

Source: Pinterest
Molding condition refers to the chamber temperature, injecting velocity, mold temperature, and other parameters that are adjusted in a molding machine to produce the desired moldings. The number of possible configurations of conditions is limitless. The looks, measurements, and mechanical characteristics of the molded products vary greatly depending on the circumstances chosen. As a result, well-tested technology and knowledge are necessary to determine the best molding conditions.

Source: Unsplash
Sprues and runners in the middle of moldings are not goods. These parts are occasionally destroyed, but in other situations, they are finely crushed and utilized as molding materials. These are known as reprocessed materials.
Because of the likelihood of degradation in different properties of the polymers due to the original molding process, reprocessed materials are generally utilized after mixing with virgin pellets. The highest permissible limit for the ratio of reprocessing materials is around 30%, since a high ratio of reprocessed elements may deteriorate the original characteristics of the polymers utilized.
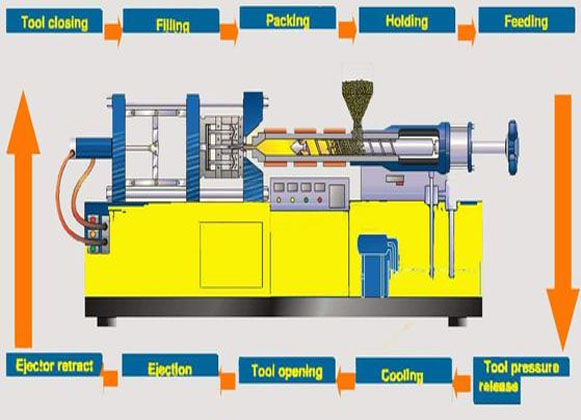
Source: Pinterest
Heating and injecting thermoplastic under stress into a confined metal mold tool is what we refer to as the injection molding process. The molten plastic cools and solidifies within the mold tooling that later opens, allowing the moldings to be extracted or retrieved for examination, delivery, or subsequent processes. The process happens in the following steps;
When the mold shuts, the Injection Molding cycle countdown begins. A hopper feeds resin pellets to the barrel. In certain situations, such as when robots are used, the cycle goes section to section, implying that the cycle starts and ends when the robot gets a new component or when the new part hits the conveyor belt.
In the mold, hot plastic is injected. The expelled air escapes via apertures in the injector pins and at the parting line when the molten material enters the mold. The layout of the runner, gate and vent is critical to ensuring that the mold is correctly filled. The screw spins to move the pellets closer to the tool.
The resultant friction, along with the barrel heaters, causes the pellets to melt. The screw is moved forth and injects the material with the speed and force required to fill the device cavity. It is critical that dislodged air exit via the apertures and parting line incorporated into the tool for this reason during this stage.
After filling the mold, the component is cooled for the appropriate time required to solidify the material. The amount of time it takes to cool depends on the type of resin being used and the density of the component. Each mold is built with inner temperature control or heating lines that circulate water via the mold to keep it at a consistent temperature.
As the component cools, the barrel screw pulls back and with it, a fresh plastic resin is moved from the materials hopper through into the barrel. The heating bands keep the container temperatures at the required level for the sort of resin to be used.
When the formed material achieves the ideal ejector degree Celcius, the machine opens and the component is forced out by the ejection rod and pins moving forward. The part might be removed by a robot, a human operator, or it can just fall into a container beneath the tool.
Even though the injection molding machine’s cycle finishes on the previous step, the operation continues. Machine operators, or robots, remove the useful pieces from the leftover debris regularly.
The runner would be the path that the plastic follows as it fills the mold chamber. To save expenses and impact on the environment, numerous runners are crushed and recycled. After that, the usable components are measured, numbered, and packed for assembling or shipment.
So that’s the fundamental Injection Molding Process. Each day, a plastic injection molding company team should engage their clients to help them identify the fundamental process they use to manufacture high-quality products. This helps keep the client(you) updated on any changes to the procedures. Therefore, you should engage a plastic injection mold maker that keeps you well informed on such details.
Since the accuracy and speed with which items may be manufactured, injection molding has an edge over other techniques. So far, no other technique can match the quality and uniformity of this technique when molding plastic.

It is dangerous to make use of components after they’ve been manufactured without encasing them with plastic. It’s essential to encase these components to make

Transparent plastic is being used in virtually every industry and this is because of its capacity to allow you see through and its ease of

Plastic is a common material used in the production of objects that can be used in homes, the automobile industry, and virtually all sectors. It

Basically, there are two kinds of plastics – thermoplastic, and thermosets. But the majorly talked about kind is the thermoplastic because of its versatile and
+86-755-8524 1121
marketing@rydtooling.com
No. 2, HongKan 1st Road, YanChuan Community, YanLuo Street, BaoAn District, ShenZhen City, China. Post Code 518105.
Subscribe to our newsletter to get manufacturing news and updates!
