What goes into creating an Elite Cooler? To ensure high ice retention, there must be a lot of insulation. However, the insulation must go someplace. The best bet is between the cooler’s tough plastic walls. So, what is the best method to go about building those walls? It’s time to weigh the pros and drawbacks of roto molded vs. injection-molded coolers.
If you’re thinking about making a plastic product, you’ve probably wondered what the distinctions are between injection molding and rotational molding. How then do they compare in terms of cost, consistency of manufacturing, materials, and design flexibility? Before we can compare the benefits of injection molding with roto-molding, we must first evaluate both methods.
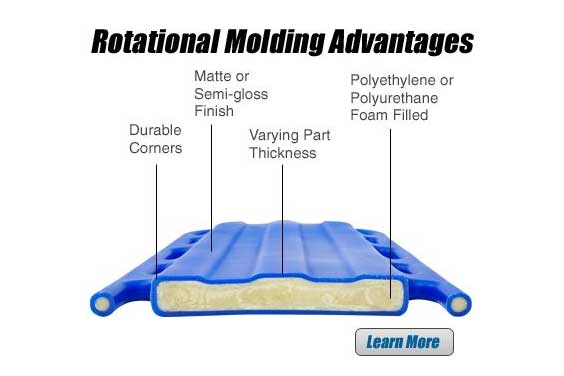
Roto-molding is a manufacturing method used to create hollow components of any size. Roto-molding may be used to produce large plastic pieces at a low cost. Initially, resins or polymers (in powder form) are injected into a hollow-shaped mold. The mold is then heated and carefully turned in vertical and horizontal planes. Because of the continual heating and turning, the resin melts and distributes uniformly throughout the inside surface of the mold.
This method yields a pre-designed component with consistent wall thickness. Since more material tends to gather at the edges and corners of the mold, the corners of a rotomolded item will have denser walls. The original iteration of Elite Coolers had all been rotomolded. The rotomolding method gave these coolers exceptional durability, and the 2″ of polyurethane insulating foam gave them outstanding ice retention.
Rotational molding elements are more confined to poly-based resins, such as polyethylene, polycarbonate, polyurethane, and polyamides, to mention a few: Nylon and plastisols are other materials that can be utilized. Before they can be utilized, these polymers must be crushed to a very fine powder. In terms of constraints, some forms and features are difficult to include, thus anything more complicated than a simple design may impede manufacturing.
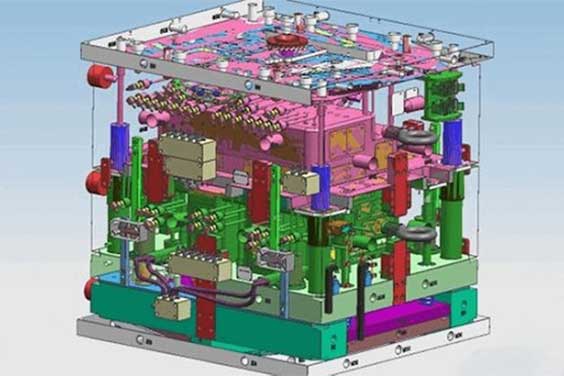
Injection molding is the process of injecting a molten plastic mixture into a firmly held mold cavity. Once injected, the plastic is heated and cools to adopt the shape of the mold. The mold may be created and built to fit any form or size of the finished object that you are attempting to make. Creating a mold is a complicated, high-skilled procedure.
The mold is made of either aluminum or steel. Molds can be constructed to make identical copies of a single item or to produce numerous pieces that fit together. Injection molding is utilized when identical copies of the same object must be produced in huge quantities.
Injection molding is a more cost-effective method for mass manufacturing. Injection molding allows for more products to be produced on the manufacturing line.


Rotomolding results in a more uniform distribution of the plastic substance. As a result of this technique, the finished product is tougher, more versatile, and more durable. Products designed for usage in harsh conditions or at high temperatures will be less likely to shatter or fracture if the roto-molding process is employed. The reason for this is that larger thickness walls at the corners and edges eliminate stress areas in a rotomolded object.
The producer can obtain a uniform wall thickness by using roto-molding. Injection molding depends on pressure to drive molten plastic through, therefore the wall thickness is not as consistent. There will be no separating lines or weld lines on the exterior of a rotomolded product. Injection molding, on either hand, will produce surface flaws that cannot be prevented.
Just before the roto-molding process has begun, it is possible to add elements such as threads and subsurface pipes to the mold. Instead of attaching labels after the forming process, serial numbers and barcodes could be molded further into a product’s shell. Rotomolding allows for the production of complicated forms in a single piece. With injection molding, it is possible to create several parts of the same item and then assemble everything.
Complex mold designs are possible using injection molding. As a result, injection molding may be used to create items with complicated forms and patterns. Injection molding is widely used in the manufacture of toys, bottle caps, handles, and some kitchen appliances.
Injection molding also allows for a wider choice of materials to be used with the mold. Rotomolding is often limited to poly-based polymers and polyamides. These materials must be crushed to a powder. Furthermore, the polymers used in injection molding are less expensive than the compounds used in rotomolding resins.
Now, judging by the information above, one would conclude that injection molding takes a higher position than rotomolding in the production of coolers. However, we strongly advise against choosing a particular process over the other, without gauging the needs of your project. So consult a professional injection mold manufacturer for proper processes to find one that suits your project’s needs.
+86-755-8524 1121
marketing@rydtooling.com
No. 2, HongKan 1st Road, YanChuan Community, YanLuo Street, BaoAn District, ShenZhen City, China. Post Code 518105.
Subscribe to our newsletter to get manufacturing news and updates!
