You might have heard of the term thermoplastic molding and are wondering what it’s about. Or maybe you’ve not heard of it before, but are curious about the various forms of molding that are relevant to the manufacture of the products you deal with. This guide walks through the details of thermoplastic molding, giving information on the very details that make the process efficient.
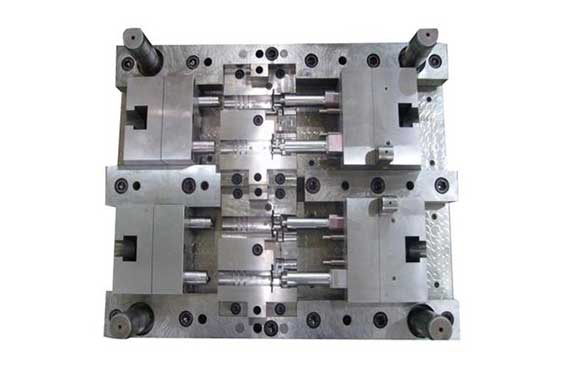
Thermoplastic injection molding is a production method that uses plastic resin to insert into a pre-made mold to generate completely functional parts. Rapid injection molding is a subcategory of thermoplastic injection molding that is best used for fine-tuning prototypes before a product is approved for manufacturing. Another subgroup, production injection molding, is best suited for large quantities of goods.

As previously said, thermoplastic injection molding entails injecting a resin into an already constructed mold to manufacture pieces in the mold’s shape. But first, let’s take a deeper look at how the system works:
This method, also known as “thermoplastic molding” or “thermoplastic injection molding,” involves the injection of molten polymer (thermoplastic substance) into a mold at increased pressure. The injection tools are created using a highly particular approach. Aluminum (rather than the more typically utilized steel) provides for lower investment costs since it can be produced more quickly.
The cost of the mold is determined by the number of cavities and the intricacy of the forms of the molded item. Following the creation of the mold, the plastic material is added under constant pressure by the injection molding machine.

Every manufacturing method has advantages and disadvantages. Before we get into the drawbacks, here are a few of the benefits of thermoplastic injection molding:

As previously said, every manufacturing method has advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of the disadvantages of thermoplastic injection molding:
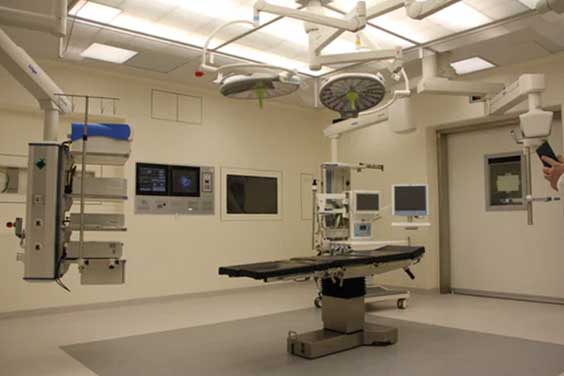
With the proper material, this method enables the manufacture of tiny series. The applications of thermoplastic injection in the plastics sector are quite diverse, encompassing the automotive, package, medical, and electronics industries in particular. A thermoplastic injection can meet regulatory standards and restrictions in an area that requires several tests and certifications, such as the medical sector.
The pieces produced are functionally equivalent to those manufactured in series. Furthermore, the thermoplastic injection manufacturing process is utilized to create parts that are either very small, like electrical components, or very big, like vehicle body pieces.

We’ve already discussed how thermoplastic injection molding can manufacture parts with high precision, making it excellent for both prototype and production runs. However, to create the finest possible components, product design must fulfill minimum and maximum thickness criteria.
The thermoplastic injection molding method, in particular, can produce parts with a tolerance of 0.2 mm. Furthermore, the technique is capable of producing more sophisticated components with tolerances as close to 5 micrometers in diameter and longitudinal characteristics. Surface finish accuracy generally ranges between 0.5 and 1 micrometer.
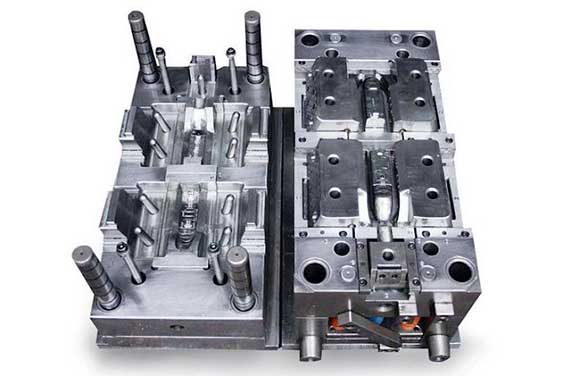
Almost any engineering-grade plastic resin may be used for thermoplastic injection molding. But that doesn’t even take into account more generic resins. Engineer-grade resins are generally used to build final prototypes before manufacturing, whereas generic resins are used to produce early iterations or less important elements of a product.
As previously stated, the wide range of plastic resins that may be produced by thermoplastic injection molding enables product creators to experiment with diverse components and surface treatments for their goods.
To summarize, thermoplastic injection molding may be used for prototype, short and long-run production owing to its speed, completed component quality, and wide range of basic and engineering-grade materials that can be used. However, like with any manufacturing process, errors might occur, potentially delaying your product delivery. That is why it is critical to work with a reputable, experienced firm for your part production requirements.
+86-755-8524 1121
marketing@rydtooling.com
No. 2, HongKan 1st Road, YanChuan Community, YanLuo Street, BaoAn District, ShenZhen City, China. Post Code 518105.
Subscribe to our newsletter to get manufacturing news and updates!
